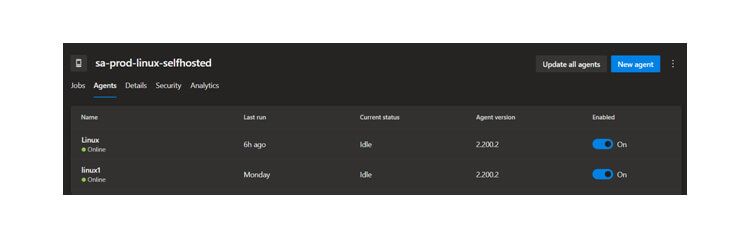
Azure DevOps Self Hosted Build Agents
4 MIN READAgent is a server with the appropriate Operating System and the tools installed and configured.
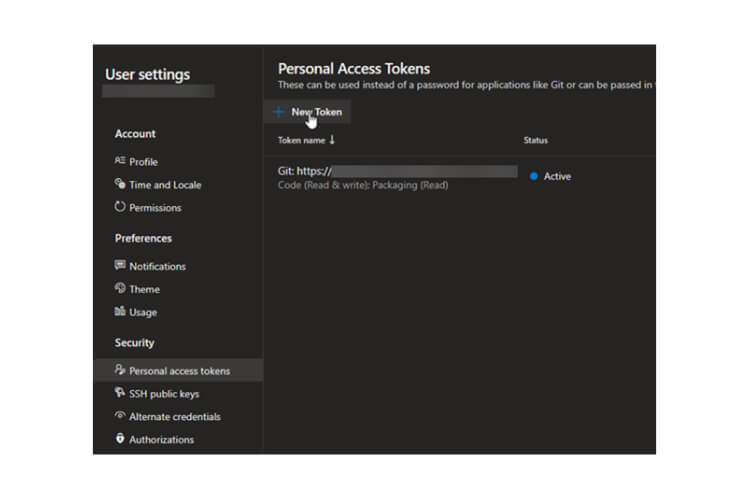
Azure DevOps Supports below two agents :
Microsoft agents – These Agents are totally manages by azure
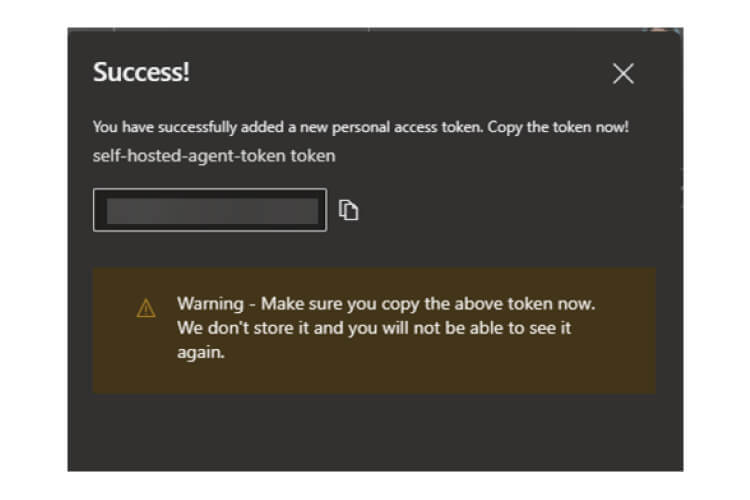
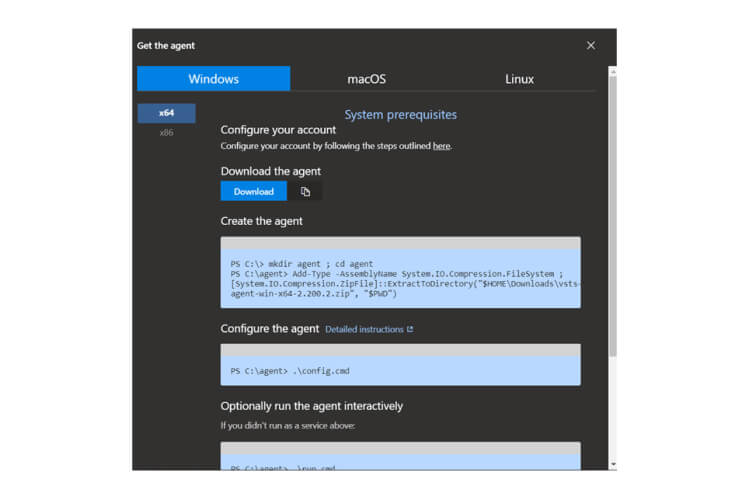
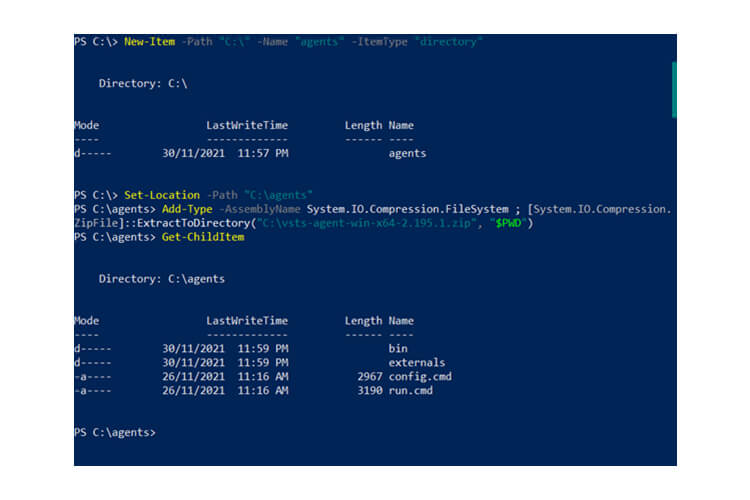
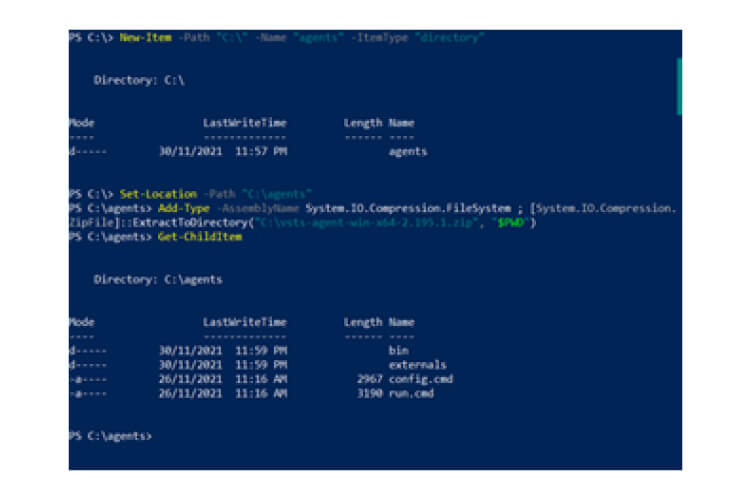
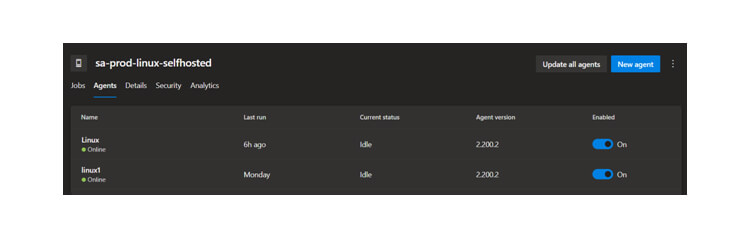
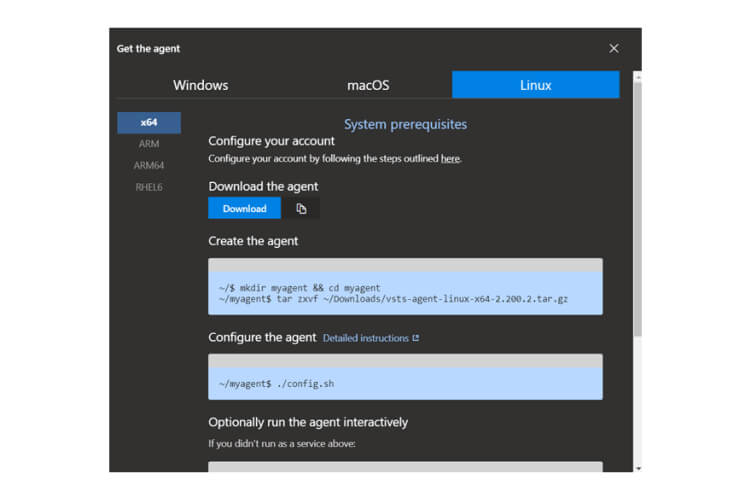
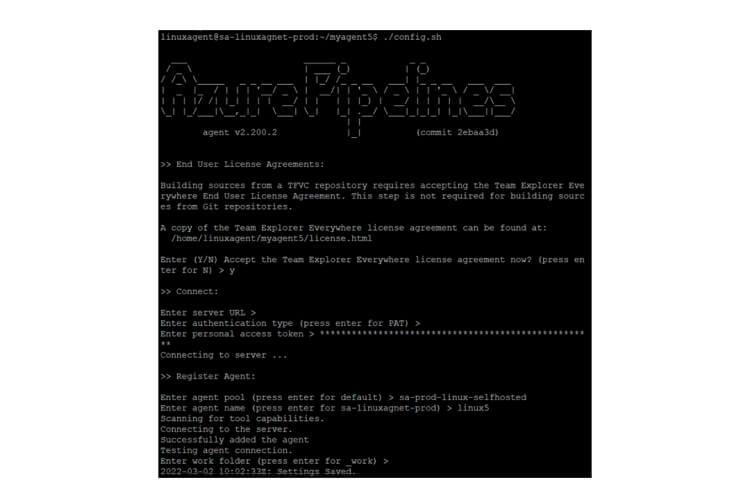
Self-Hosted Agents – These agents are configured by the user according to their needs.